Imagine growing fresh, organic vegetables while raising fish—all in one efficient, eco-friendly system. Welcome to aquaponics, a revolutionary gardening method that combines aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation). This symbiotic system uses fish waste to nourish plants, while the plants naturally filter the water for the fish. Whether you’re looking to reduce your carbon footprint or enjoy homegrown food, aquaponics offers an innovative and sustainable solution.

🌟 Why Choose Aquaponics?
Aquaponics isn’t just a gardening trend—it’s a sustainable lifestyle choice. Here’s why:
- Eco-Friendly: Uses 90% less water compared to traditional soil farming.
- Efficient: Produces both vegetables and fish in a single system.
- Pesticide-Free: A natural ecosystem eliminates the need for harmful chemicals.
- Space-Saving: Ideal for urban gardens or small spaces, with vertical systems maximizing productivity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Aquaponics System
1️⃣ Select the Perfect Location 🏡
Choosing the right spot is key to a thriving system:
- Sunlight: Ensure 6–8 hours of direct sunlight for plant growth. For indoor setups, invest in LED grow lights for optimal light exposure.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a stable temperature—most plants and fish thrive between 68°F and 86°F (20–30°C).
- Power and Water Access: Place the system near a power outlet and water source for convenience.
- Space Efficiency: Use vertical setups or compact designs for smaller areas.
2️⃣ Set Up the Fish Tank 🐠
The fish tank is the heartbeat of your aquaponics system:
- Tank Size: Beginners can start with a 100-gallon tank for better water quality stability.
- Material: Use food-safe materials like plastic or fiberglass.
- Fish Selection: Choose hardy species such as tilapia, koi, or goldfish. For colder climates, try trout or perch.
- Placement: Position on a sturdy surface to support the water weight.
3️⃣ Install the Grow Bed 🌱
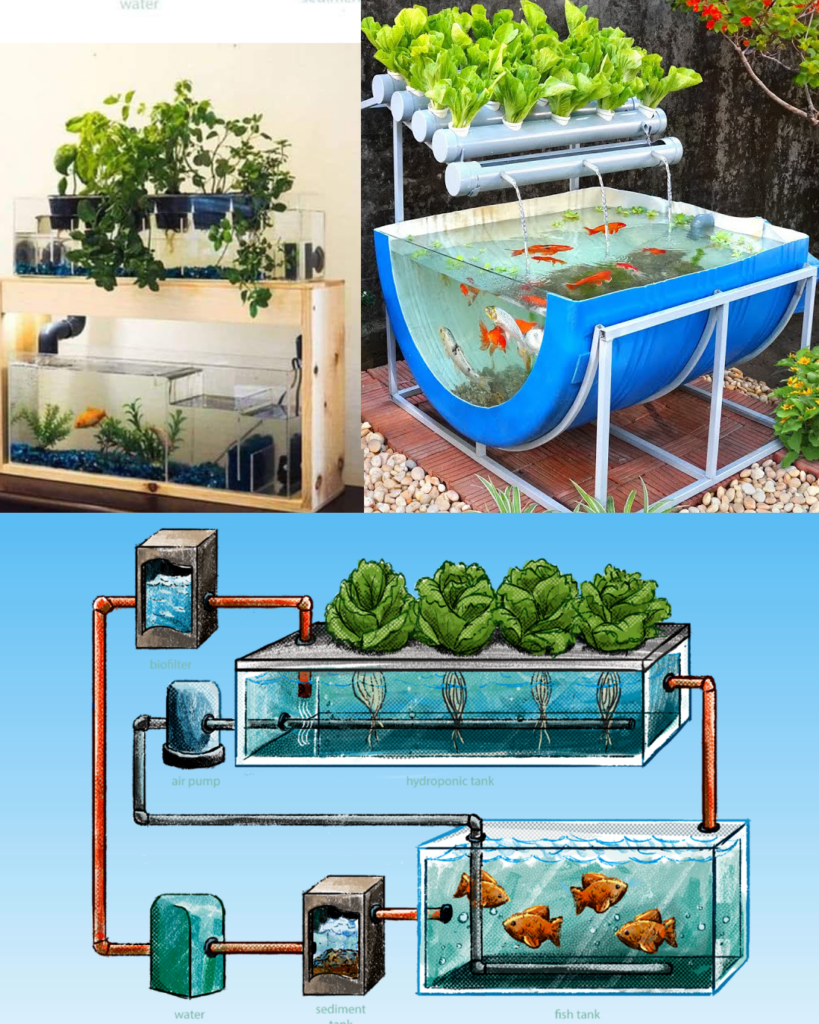

Your plants will thrive in the grow bed, which filters the fish tank water:
- Positioning: Place above the fish tank for gravity-fed water return.
- Growing Medium: Use expanded clay pebbles, lava rocks, or gravel to support roots and bacterial growth.
- Size: Maintain a grow bed size roughly half the volume of the fish tank.
- Depth: Ensure at least 12 inches of depth for root growth and nutrient absorption.
4️⃣ Connect a Water Pump and Plumbing 🔄
A reliable pump ensures seamless water circulation:
- Pump Power: Choose a pump that can cycle the tank’s water volume at least once per hour.
- Plumbing Setup: Use food-grade tubing to connect the pump to the grow bed. Add a bell siphon for efficient water flow and prevent overflooding.
- Backup System: Install solar panels or battery backups to keep the pump running during power outages.
5️⃣ Cycle Your System 🔬
Before adding fish and plants, establish a healthy bacterial ecosystem:
- Cycling Process: Introduce ammonia (from fish waste or pure ammonia) to build nitrifying bacteria. These bacteria convert toxic ammonia into nitrites and then nitrates—nutrients essential for plants.
- Monitoring: Use water test kits to check ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. Cycling usually takes 4–6 weeks.
- Optimal Conditions: Maintain a water temperature of 77°F–86°F (25–30°C) for faster cycling.
6️⃣ Add Fish and Plants 🌿🐟
With the system cycled, it’s time to introduce life into your aquaponics setup:
- Fish Acclimation: Gradually introduce fish by floating their transport bag in the tank for 15–20 minutes to equalize temperature.
- Planting: Opt for easy-to-grow plants like lettuce, basil, spinach, or tomatoes. Start with seedlings for quicker establishment.
- Spacing: Allow sufficient space between plants to prevent overcrowding.
7️⃣ Monitor and Maintain 🛠️
A thriving aquaponics system requires regular care:
- Water Quality: Test pH (6.8–7.2), ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels weekly. Adjust pH naturally using crushed coral (to raise) or vinegar (to lower).
- Feeding: Feed fish sparingly to prevent leftover food from polluting the water.
- Plant Health: Watch for signs of nutrient deficiencies or pests and prune regularly.
- Equipment Check: Inspect pumps, tubing, and grow beds for clogs or leaks.
💡 Pro Tips for Success
- Diversify Your Crops: Combine fast-growing greens with fruiting plants like peppers or strawberries for variety.
- Water Temperature Control: Use heaters or cooling fans to maintain stable conditions, especially in extreme climates.
- Natural Pest Control: Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs to handle pests without chemicals.
🌟 The Benefits of Aquaponics
- Eco-Conscious Farming: Use 90% less water than traditional soil farming.
- Self-Sufficiency: Grow fresh, organic food at home, reducing reliance on store-bought produce.
- High Yields in Small Spaces: Perfect for urban areas, balconies, or small yards.
- No Fertilizers Needed: Fish waste provides all the nutrients plants need.
⚠️ Challenges to Consider
- Initial Investment: Equipment like tanks, pumps, and grow lights can be expensive.
- Learning Curve: Understanding water chemistry and system balance takes time.
- Electricity Dependence: Backup systems are crucial for uninterrupted operation.
Start Your Aquaponics Journey Today
Aquaponics is more than a gardening method—it’s a sustainable lifestyle. By growing your own food and raising fish, you can reduce waste, save resources, and enjoy the satisfaction of a self-sufficient system.
🌱 Ready to get started? Build your system, choose your fish and plants, and experience the magic of aquaponics firsthand.
📌 Discover more about sustainable gardening techniques and tips to maximize your aquaponics success in our upcoming guides!